What is Regenerative Braking?
Regenerative Brake
Regenerative braking is a braking technology used in electric and hybrid vehicles. This system converts the kinetic energy generated when the vehicle slows down or brakes into electricity, charging the vehicle battery. In traditional braking systems, kinetic energy is lost by converting it into heat when the brakes are applied. However, with regenerative braking, this energy can be reused, which both saves energy and increases the range of the vehicle.
How Does It Work?
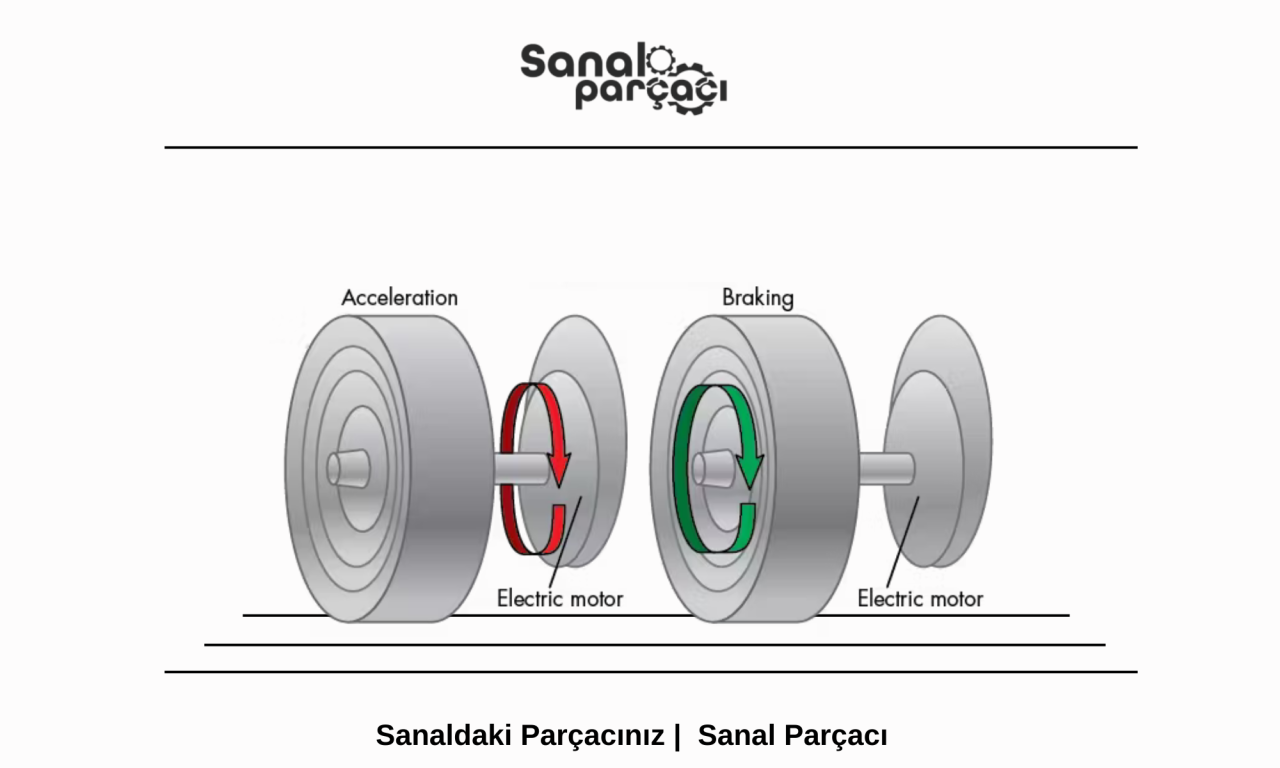
Regenerative braking works on the principle of the electric motor working in reverse. The motors used in electric vehicles are used to both generate power and collect energy during braking. When the brakes are applied or your foot is removed from the gas pedal, the motor switches to generator mode. The generator converts the vehicle's kinetic energy into electrical energy and sends this energy back to the battery.
What are the advantages?
1. Energy Efficiency: Regenerative braking increases energy efficiency by recovering the vehicle's kinetic energy, thus extending the vehicle's range and ensuring the battery lasts longer.
2. Less Wear: Compared to traditional braking systems, regenerative brakes cause less mechanical wear because the braking process is largely done by the electric motor and the brake pads are used less.
3. Less Heat Generation: Because regenerative braking converts energy into electricity, it reduces the amount of heat generated during braking. This can extend the life of the brake system.
4. More Environmentally Friendly: Energy-saving regenerative braking reduces the vehicle's overall energy consumption, contributing to lower carbon emissions. This stands out as an environmentally friendly technology.
What are the disadvantages?
1. Limited Braking Power: Regenerative braking alone cannot meet all the braking force. Therefore, vehicles usually have conventional braking systems together with regenerative braking.
2. Cost: Regenerative braking systems can be costly due to their complex structure. In particular, the repair or maintenance costs of this system are higher than traditional braking systems.
3. User Experience: Regenerative braking may affect the driving experience. In particular, some drivers may report that this system feels different from the braking sensation they are used to.
In Which Vehicles Is It Used?
Regenerative braking is particularly common in electric and hybrid vehicles. Fully electric vehicles such as the Tesla, Nissan Leaf, BMW i3, and hybrid vehicles such as the Toyota Prius have regenerative braking technology as standard. It is also used in Formula 1 racing.
Regenerative braking has an important place among the sustainable automotive technologies of the future. It is being used in more and more vehicles due to its energy efficiency and environmental friendliness. As technology develops, the effectiveness and prevalence of regenerative braking will increase even more.
